Shockwave Therapy vs PRP: Which Treatment Is More Effective for Tendon and Soft Tissue Injuries?
Introduction
Tendinopathies and overuse injuries are common in both athletic and non-athletic populations. With new regenerative treatments on the rise, two options often discussed are shockwave therapy (ESWT) and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections.
At Tensegrity Sports Clinics, we’re frequently asked: “Which one works better?” Let’s break down the science, clinical evidence, and practical considerations to help guide your decision.
How PRP Therapy Works
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is derived from the patient’s own blood. After centrifugation, a high concentration of platelets is injected into the injured tissue. PRP aims to:
- Stimulate cell proliferation
- Release growth factors (e.g., PDGF, TGF-β, VEGF)
- Accelerate collagen and soft tissue repair
While PRP is biologically powerful, it’s invasive, often requires ultrasound guidance, and comes with higher cost and variability in outcomes.
How Shockwave Therapy Works
Shockwave therapy is a non-invasive, device-based treatment that uses high-pressure sound waves to stimulate biological repair. It:
- Promotes neovascularisation (blood vessel formation)
- Increases collagen production
- Breaks down calcific deposits
- Modulates pain pathways through hyperstimulation analgesia
It’s painless to mildly uncomfortable and does not require downtime.
What the Research Says
Systematic Review: PRP vs Shockwave
Study: Li et al. (2019)
Title: “Comparison of PRP and ESWT in the treatment of chronic tendinopathies: a meta-analysis”
Published in: Clinical Rehabilitation
Key Findings:
- No significant difference in long-term pain or function scores between PRP and shockwave therapy.
- Shockwave had lower cost, fewer side effects, and quicker return to activity.
Patellar Tendinopathy Study
Study: Dragoo et al. (2014)
- PRP and ESWT both improved outcomes in athletes with jumper’s knee.
- However, PRP required 3–6 weeks of limited activity post-injection.
- Shockwave allowed faster reintegration into sport.
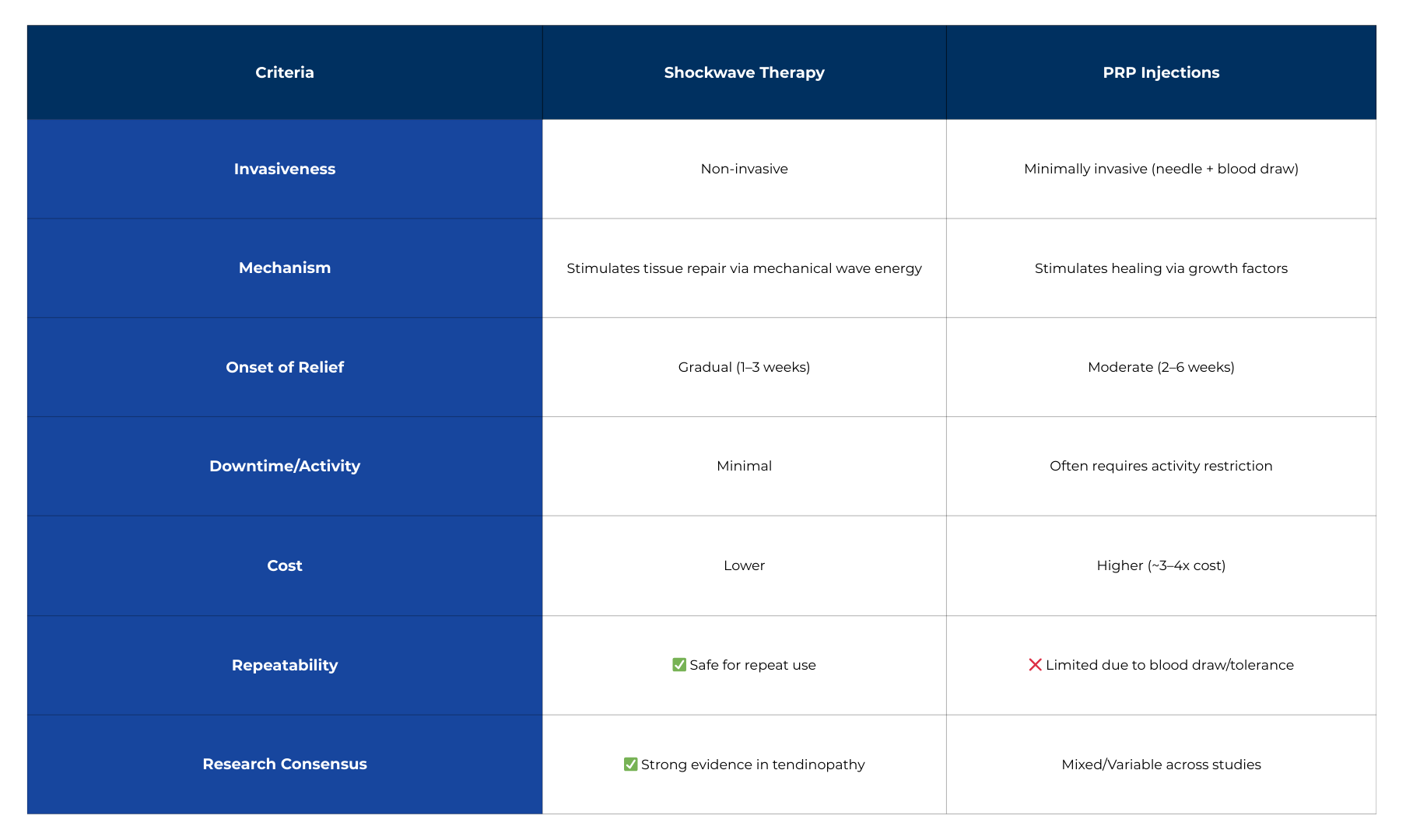
Comparison Table: Shockwave Therapy vs PRP Injections
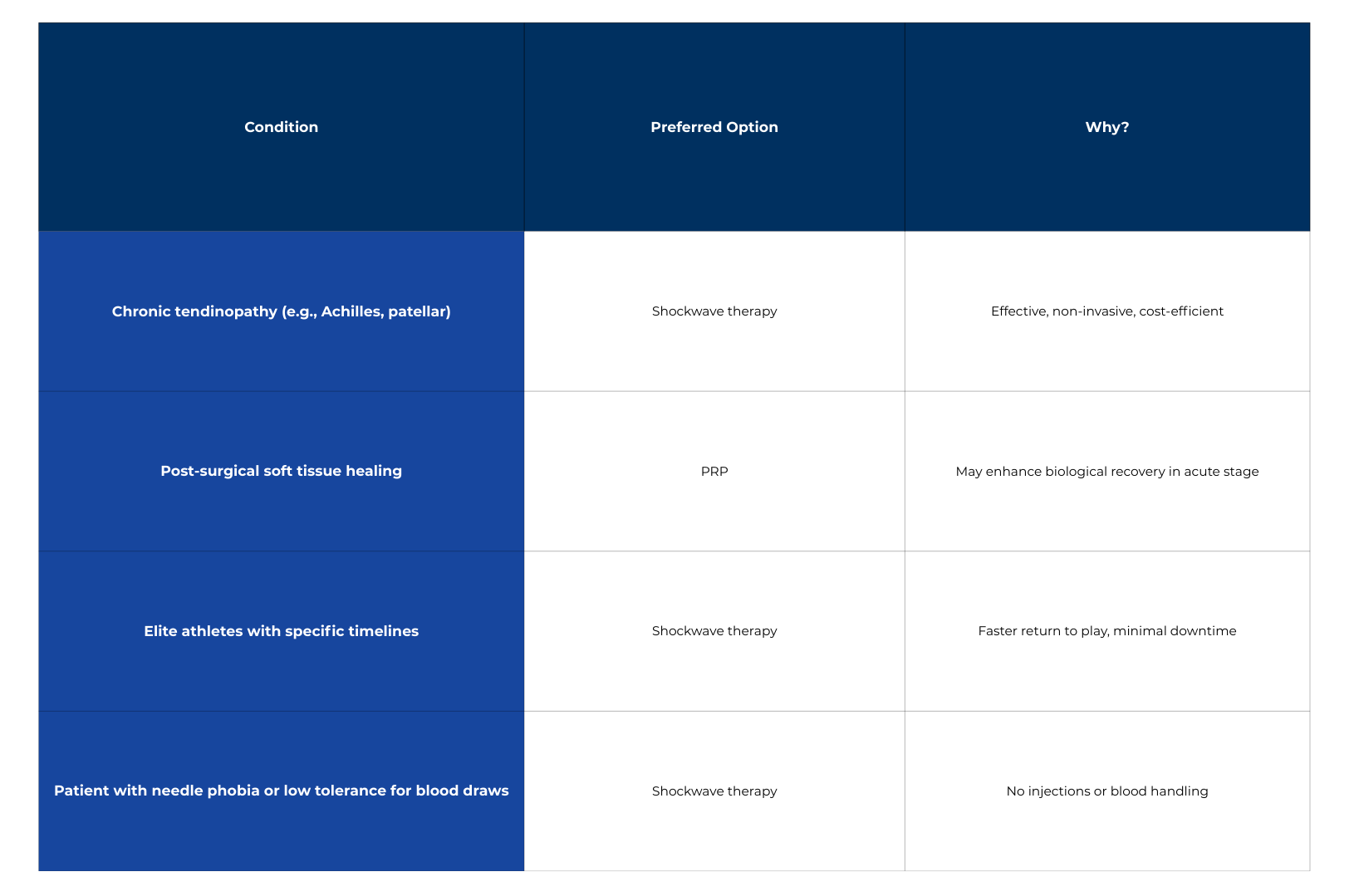
Clinical Scenarios: When to Choose What?
Conclusion
Both PRP and shockwave therapy stimulate tissue healing — but they differ in invasiveness, cost, accessibility, and downtime. For most soft tissue injuries, shockwave therapy offers an effective, lower-risk, and more affordable option backed by strong evidence.
Our experienced practitioners at Tensegrity Sports Clinics Sydney can assess your condition and help you choose the best approach based on your health history, recovery goals, and sport-specific needs.
